What is Concrete, When Did They Start Using It, and How Has It Changed Over Time?

What is Concrete: Composition and Purpose.
Concrete is an artificial stone building material formed by hardening a mixture of cement, water, sand, gravel (or crushed stone), and special additives and plasticizers. It is the foundation of modern construction due to its strength, durability, and versatility.
History of Concrete: Who and When Invented Concrete.
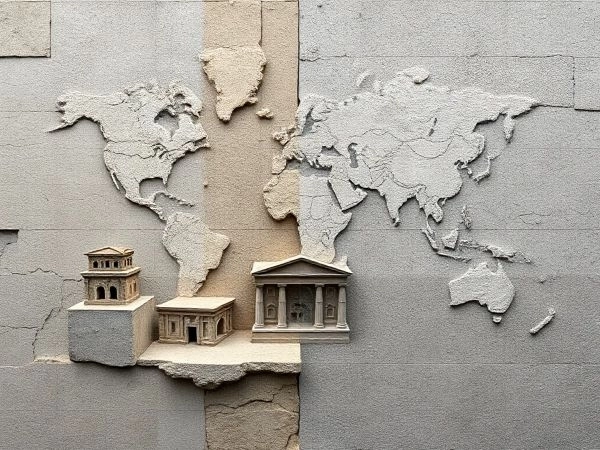
Concrete in Ancient Civilizations.
The first concrete-like mixtures were used in Ancient Egypt, Mesopotamia, and China:
- Egyptians (≈3000 BC) used lime and gypsum for pyramid construction.
- In China, mineral binders with rice glue were used in building the Great Wall.
- Mesopotamians strengthened bricks with clay and ash mixtures.
Although not modern concrete, these technologies laid the foundation for its history.
Concrete in the Roman Empire.
The true breakthrough came from the ancient Romans, who created Roman concrete (opus caementicium) — a mixture of lime, volcanic ash (pozzolana), water, and stone fragments. This concrete was very strong and durable.
Example — the Pantheon in Rome (125 AD): its dome is made of concrete and remains the largest unreinforced concrete dome in the world.
From the Middle Ages to Modern Times: How Concrete Evolved?
After the fall of the Roman Empire, knowledge of concrete was nearly lost. Medieval Europe mainly used lime mortars. The technology revival began only in the 19th century.
In 1824, Englishman Joseph Aspdin patented Portland cement — the main component of modern concrete. Since then, concrete construction technology has rapidly developed.
Modern Concrete: Innovations, Additives, and Fibers.
New Types of Concrete.
Modern concrete differs greatly from historical variants due to engineering and technological advances. Today, there are dozens of concrete types with various properties:
- Reinforced concrete — concrete reinforced with steel bars, widely used in construction.
- High-strength concrete — withstands heavy loads, used in bridges and skyscrapers.
- Ultra-lightweight concrete — reduces structural weight.
- Self-compacting concrete (SCC) — flows easily without vibration, fills complex molds.
- Green concrete — incorporates recycled materials and has a low carbon footprint.
- 3D printing concrete — innovative material for building structures without traditional formwork.
Chemical Additives and Plasticizers in Concrete.
Chemical additives allow control over the properties of the concrete mix:
- Plasticizers and superplasticizers — increase workability without strength loss.
- Accelerators — reduce setting time.
- Retarders — extend working time.
- Air-entraining agents — improve frost resistance.
- Water repellents — reduce water absorption and increase durability.
Polypropylene Fibers in Concrete.
One modern method to improve concrete is adding polypropylene fibers. They:
- reduce microcrack formation during shrinkage;
- increase crack resistance;
- improve impact and fire resistance;
- are used in industrial floors, tunnels, and 3D printing.
The Role of Concrete in the Modern World.
Today, concrete is the most widely used construction material worldwide. It is applied in:
- residential construction;
- industry;
- infrastructure (bridges, roads, airports);
- hydraulic structures.
Global concrete production exceeds 10 billion tons per year.
Conclusion:
Concrete has evolved from primitive lime mixtures to a high-tech material that can be customized in properties, reinforced with fibers, 3D-printed, and made environmentally friendly. Thanks to ongoing innovations, concrete remains the foundation of modern infrastructure and construction.
In Ukraine, innovative approaches to improving concrete and enhancing its properties are implemented by the company Coalida, operating under the brand MTC Concrete. The company specializes in producing various concrete additives, including plasticizers, micro reinforcement with polypropylene fibers, and other advanced chemical components. MTC Concrete supports the latest global standards and offers effective solutions for residential, industrial, and infrastructure construction in Ukraine.